Construction of the Tiangong Space Station began with the launch of its core module, Tianhe (“Harmony of the Heavens”), in April 2021. Tianhe serves as the station’s command center, providing living quarters for up to three astronauts and housing essential life support, power, and propulsion systems. The core module is complemented by two laboratory modules: Wentian (“Quest for the Heavens”) and Mengtian (“Dreaming of the Heavens”), launched in July and October 2022, respectively. Together, these three modules form a T-shaped structure, with the core at the center and the labs on either side.
A planned space telescope module, Xuntian, will also be attached to the station in the future, expanding its scientific capabilities.
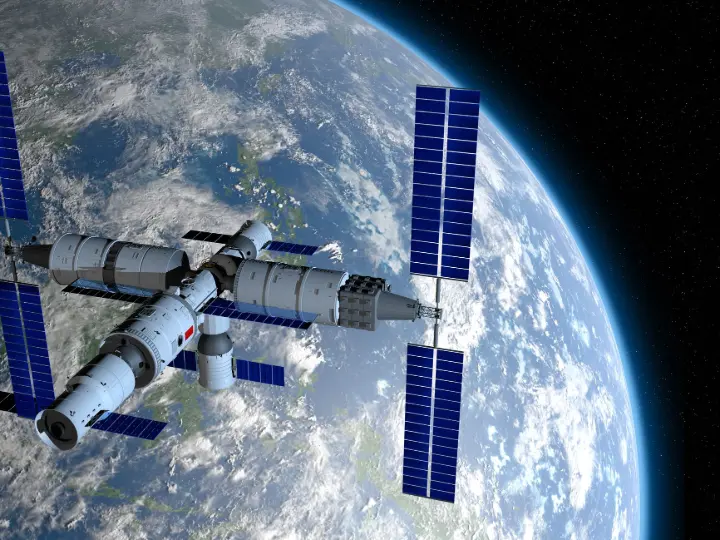

Gravity in space or not? A viral video of China's Tiangong Space Station has sparked a heated online debate.
In the now-viral clip, an open glass of water was shown sitting still on a table, prompting netizens to dub the video as fake, as the liquid should not be staying that still in microgravity.
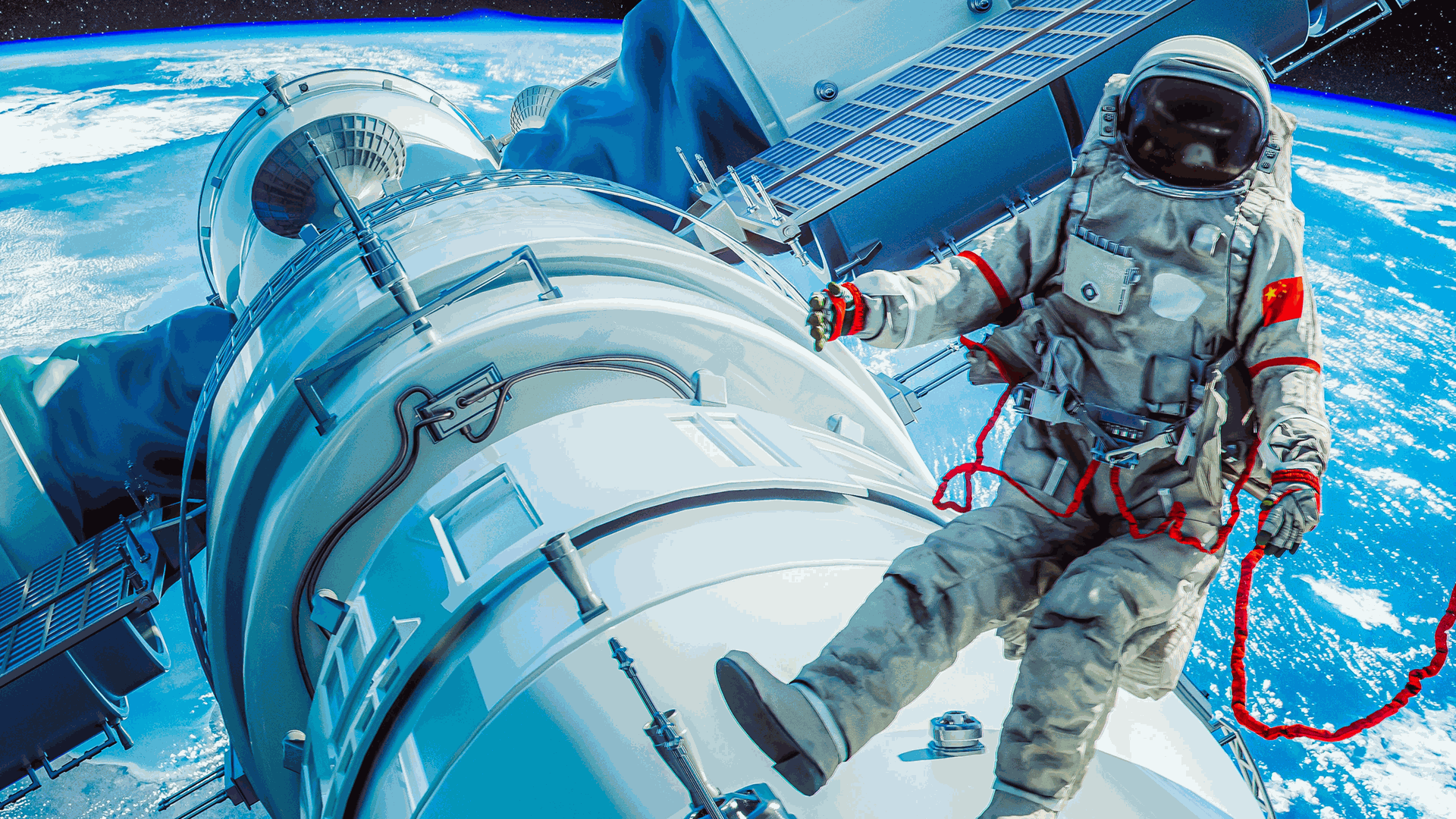
Cost: 6,000 crores CNY (2021)
Launch date: 29 April 2021
Speed on orbit: 7.68 km/s
Max speed: 27,650 km/h
Orbit height: 425 km
Size and Capacity
The Tiangong Space Station is significantly smaller and lighter than the International Space Station (ISS). With a total mass of about 66 tonnes and a pressurized volume of approximately 340 cubic meters, it is about one-fifth the mass and one-third the size of the ISS. The station can accommodate up to three astronauts for six-month stays and up to six astronauts during crew handovers.
Scientific Research and Experiments
The Tiangong Space Station is designed as an in-orbit laboratory, featuring 23 enclosed experiment racks for a wide range of scientific investigations. These experiments span fields such as:
- Space life sciences and biotechnology
- Microgravity fluid physics and combustion
- Material science in space
- Fundamental physics in microgravity
The station also includes platforms for exposed and unpressurized external experiments, allowing for unique studies not possible on Earth. Recent highlights include the discovery of a new species of bacteria, Niallia tiangongensis, aboard the Tiangong Space Station.